Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP): What is it?
Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) is the general term given to plastic polymers which are combined with fibers to produce a composite material: any material produced from a combination of two or more different material types. The fiber reinforcements offer unique and strength-enhancing properties not found in pure plastic, making it possible to create structures that are ighter and stronger than those made with plastic alone.
As FRP is generally reinforced with glass fiber it is interchangeably referred to as Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic or fiberglass. The first letter of the acronym denotes the type of reinforcing fiber used: G refers to glass fibers, C refers to carbon fibers and A stands for aramid fibers.
The Peak of FRPs: Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP)
Most FRP applications utilize glass fibers as the reinforcing material, whereas CFRP is a carbon fiber-specific composite. Carbon fiber is a fiber material produced by carbonizing acrylonitrile (PAN) fibers or pitch, a by-product of petroleum, coal, or coal tar and is classified according to the raw materials used: PAN-based carbon fiber for the former, and Pitch-based carbon fiber for the later. The impressive lightweight qualities and superior strength of CFRP makes it the popular material of choice in aviation, automobile, and sporting equipment industries.
Key Characteristics of Carbon Fiber
- One-fourth the specific gravity of iron.
- Ten times the specific strength of iron.
- Seven times the specific modulus of elasticity, compared to iron.
In addition to its renowned “strong, lightweight, and non-corrosive” properties, carbon fiber showcases a range of other features such as X-ray permeability, electrical conductivity, thermal resistance, and low expansion.
Fiber Reinforced Plastic Applications
Applications of GFRP and CFRP vary according to the unique characteristics and qualities of each material.

GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic)
Glass fiber reinforced plastic applications are extremely widespread with a long history stemming back to its industrialization in the late 1930s and 1940s.
Application
GFRP is used in many every day-use applications such as playground equipment and rides in parks and recreational facilities, or waterproofing in bathtubs, wash basins and balconies. In sporting and mobility-related industries, GFRP is employed in everything from surfboards, tennis rackets, and golf clubs to motorcycles, automobiles, ships, and trains. Moreover, as any car enthusiast would know, GFRP is the popular choice for aerodynamic parts in the automobile world.
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic)
Compared to GFRP, CFRP has a relatively short history with widespread application accelerating in the 1970s. CFRP is lighter, stronger and commands a higher market value than GFRP, leading to vast recognition and use as a high-end material.
Application
Approximately 50% of the fuselage (body) of the Boeing 787 commercial airplane is constructed with CFRP. It is also widely employed in racing car products and structural, exterior, and optional components for supercars and high-end automobiles. Woven type CFRP delivers even more formidable design and aesthetic potential, as can be in the fine textures and patterns of exterior components. CFRP is also commonly employed for satellites and rockets in the aerospace field, alongside sporting equipment applications such as cars, golf shafts, fishing rods, baseball bats, tennis rackets, and ski equipment.

Summary
This issue explores the application of fiber reinforced plastics and the differences between the two hallmark types: GFRP and CFRP. The differences are often obscure, so we hope this issue shed some light on the key points.
Related useful contents
You can explore related content by clicking on a topic of interest.
ABOUT UCHIDA - 55 years since our founding
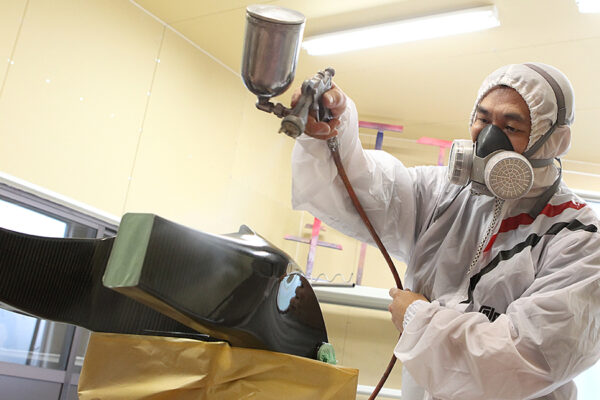
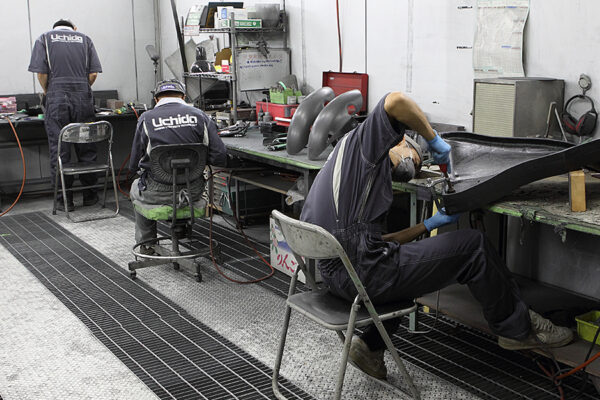
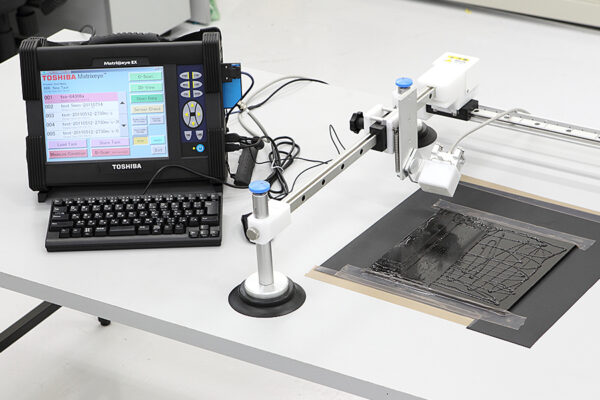
We leverage a wealth of technical expertise as a CFRP molding and processing manufacturer using FRP, GFRP, and CFRP materials. We offer a one-stop solution, encompassing design, analysis, manufacturing, secondary processing, assembly, painting, quality assurance, and testing.
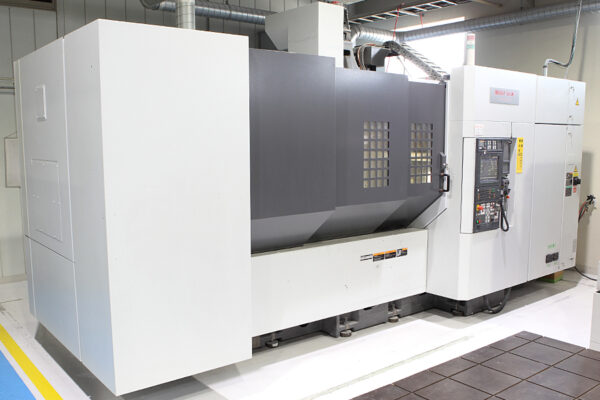
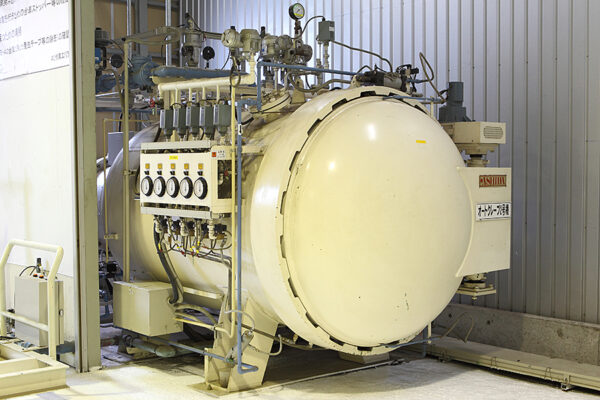
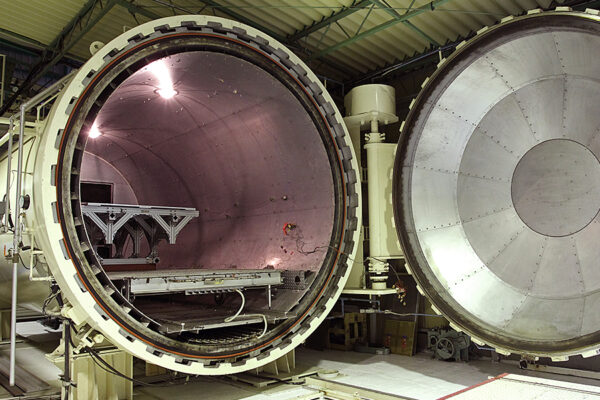
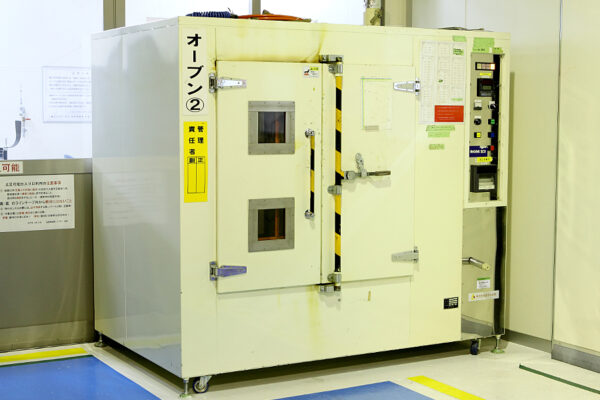
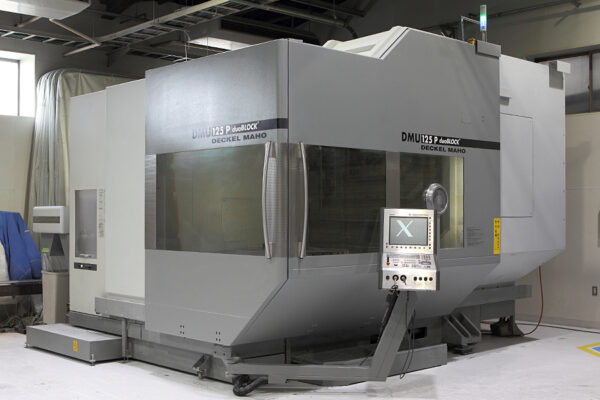
UCHIDA's equipment
We have cutting-edge equipment to ensure that we can address even the most advanced challenges of our customers.
Video Library
In the following video, we provide a detailed overview of our manufacturing process. Please feel free to watch and learn more.