Introduction
The term carbon fiber has become high-use jargon in recent years. While most people know it is a lightweight and strong substitute material for metal, frequently used in commercial planes and automobiles, that’s usually the extent of information we have. So, what else is there to know about this material?

Overview
Modern carbon fiber technology (material) originated in Japan and is now widely employed combination with a polymer plastic matrix to create composite materials known as carbon fiber reinforced plastics (composite material). In this section, we’ll discuss the molding dies used when forming/molding CFRP.
CFRP Characteristics
CFRP is distinguished by “lightweight, strong, and non-corrosive” characteristics. Read more here in our previous articles.
A Lighter and More Durable Material—CFRP
CFRP Manufacturing Methods
Although CFRP has various advantages, what manufacturing methods are utilized?
In this section, we will focus on two key topics: 1) Autoclave Molding as the leading molding technique, and 2) Prepregs, the core CFRP material used in Autoclave Molding.
Carbon & CFRP Autoclave Molding?
Prepregs: What are CFRP Prepregs?
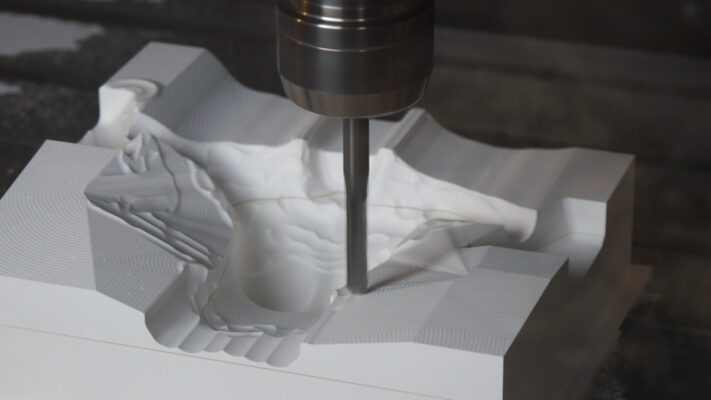
CFRP Molding Dies (Molds)
Thus far, we have explored the key characteristics of CFRP. But what about the molds required for CFRP production? In this article, we will look at the mold materials and their varying uses.
Prototype Molds (Gypsum)
Gypsum, or plasterboard, is widely used in Japan for prototype development and small-lot production (1-10 products).
First, we bond the gypsum-based board material to the through-thickness direction (Z-direction, perpendicular to the surface) of the product, to create width and then we fabricate and shape the mold in our machining center.
*This is called a straight carving mold.
After processing, we seal and finish the surface with resin and then release the mold to complete production.
Advantages
- Low coefficient of linear expansion and good compatibility with CFRP
- High machinability
- Fast turnaround (short lead time)
- Lighter and easier to handle than metal molds.
Disadvantages
- Brittle and susceptible to chipping.
- Low durability
- As an insulating material, it generally has poor heat dissipation and long mold formation times.
FRP Inverted Molding (Hand Lay-up Processing Method: GFRPs and CFRPs)
A method often used for small production lots of 30–100 products. We machine an exact duplicate of the product (called a prototype or master profile) and then use this to produce an inverted mold.
Advantages
- Low coefficient of linear expansion and good compatibility with CFRP
- High machinability
- Fast turnaround (short lead time)
- Lighter and easier to handle than metal molds.
Disadvantages
- Brittle and susceptible to chipping.
- Low durability
- As an insulating material, it generally has poor heat dissipation and long mold formation times.
FRP Inverted Molding (Hand Lay-up Processing Method: GFRPs and CFRPs)
A method often used for small production lots of 30–100 products. We machine an exact duplicate of the product (called a prototype or master profile) and then use this to produce an inverted mold.
Advantages
- Lightweight and easy to handle
- Highly durable
- Short molding times (molding according to the product material) made possible with good heat dissipation
- Hand lay-up fabrication method of master profile eliminates the need for heat-resistant materials.
- The split position (division position of the mold) can be set arbitrarily, even for complex shapes.
Disadvantages
- Comparatively high expansion–contraction during molding due to the large volume of resin used.
- Difficult to accommodate to minor profile modifications and design changes.
Summary
This article focuses on molds produced from carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP). Despite being a cutting-edge material, there is still limited understanding due to a lack of available information. The production lot volume, size of the product, and required versatility for design modifications governs which molding method we employ. Selecting the optimal method for the job is crucial and, depending on the industry or enterprise, we may even use metals to create a metal die. Ultimately, the most important factor is “what” and” how many”. Mold creation hinges on a detailed understanding of the product design aims and specifications and, thereby, must be conducted with a clear vision of the product’s key features and strengths.
Related useful contents
You can explore related content by clicking on a topic of interest.
ABOUT UCHIDA - 55 years since our founding
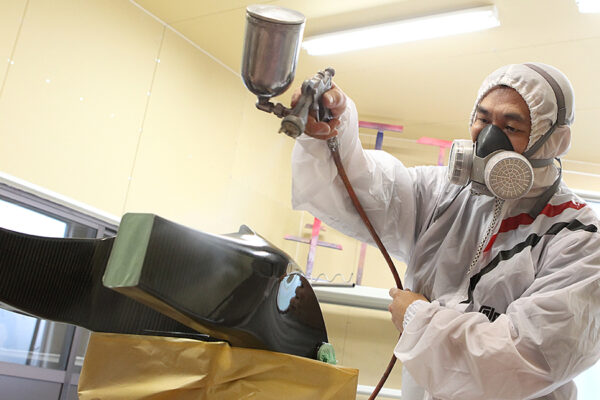
We leverage a wealth of technical expertise as a CFRP molding and processing manufacturer using FRP, GFRP, and CFRP materials. We offer a one-stop solution, encompassing design, analysis, manufacturing, secondary processing, assembly, painting, quality assurance, and testing.
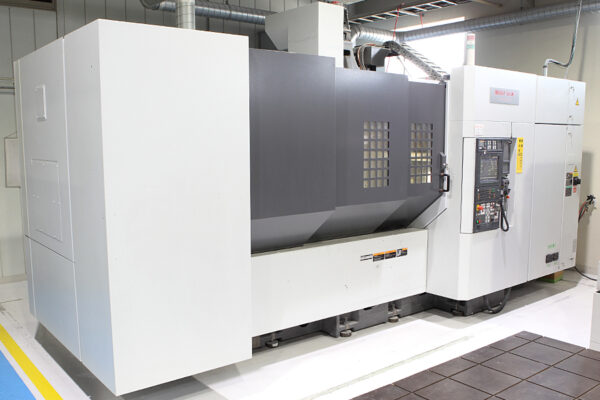
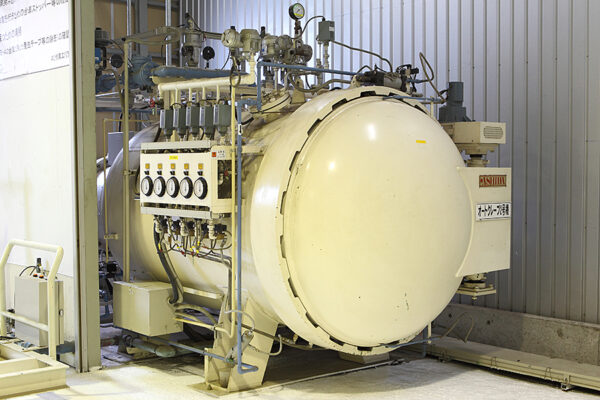
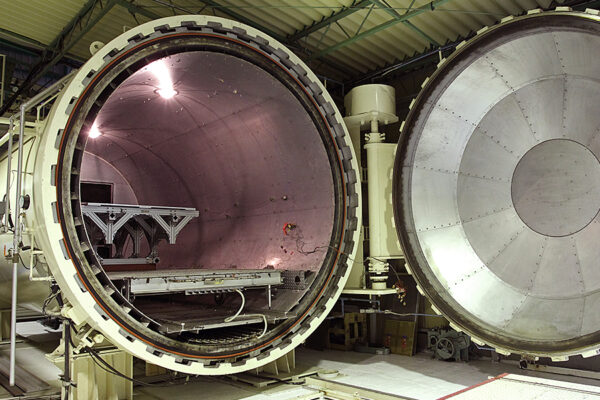
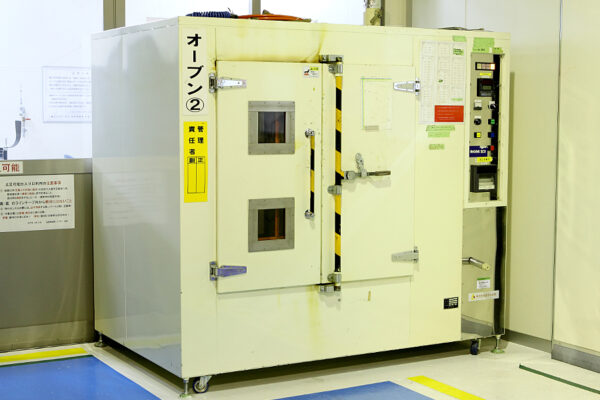
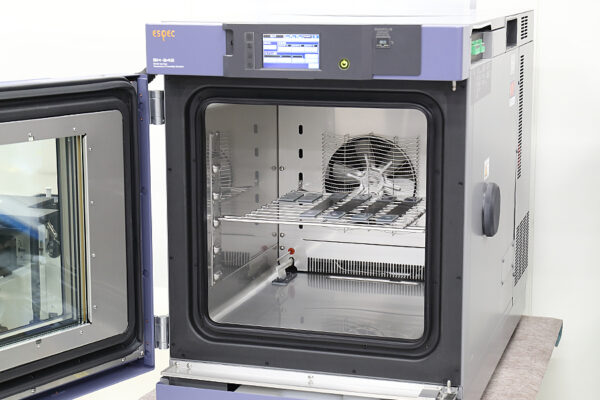
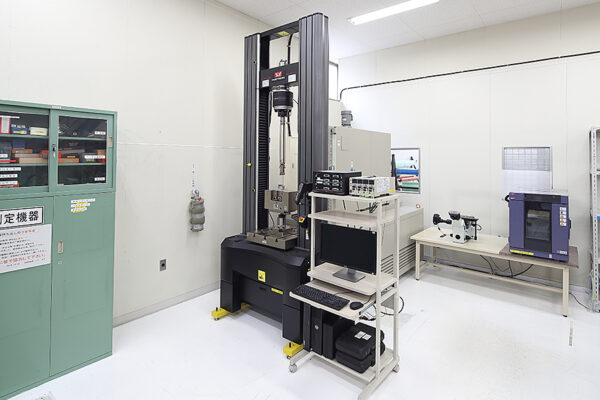
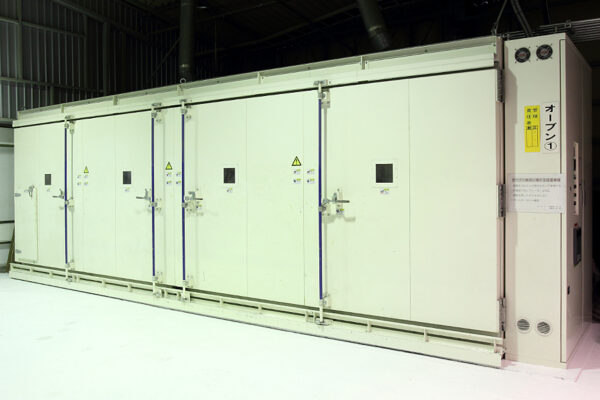
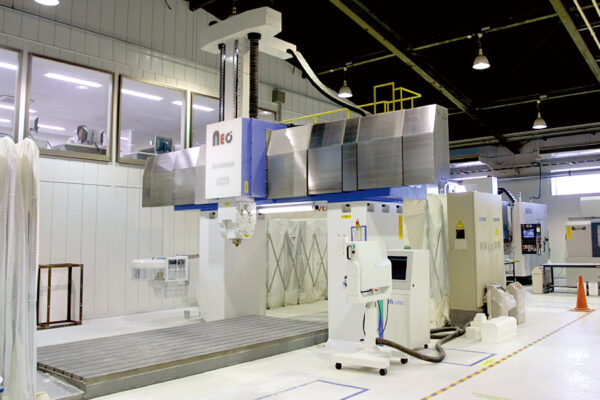
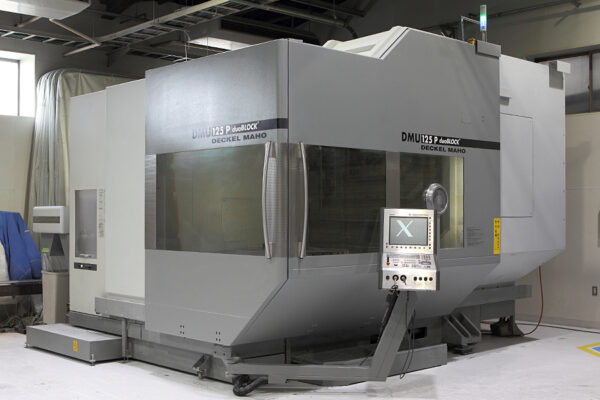
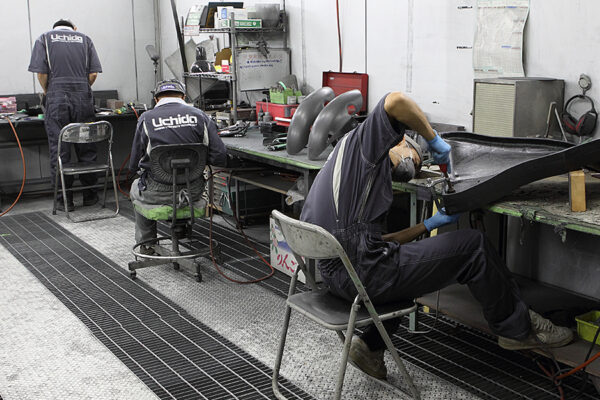
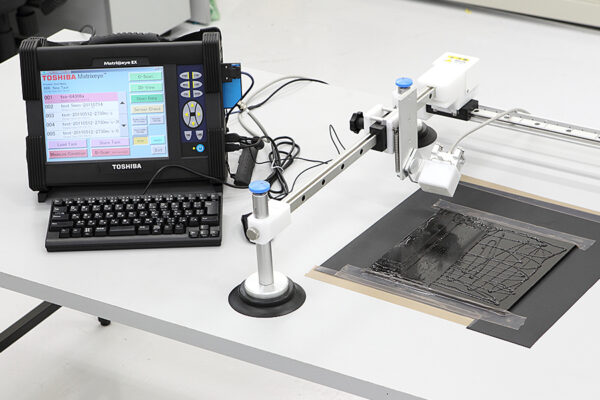
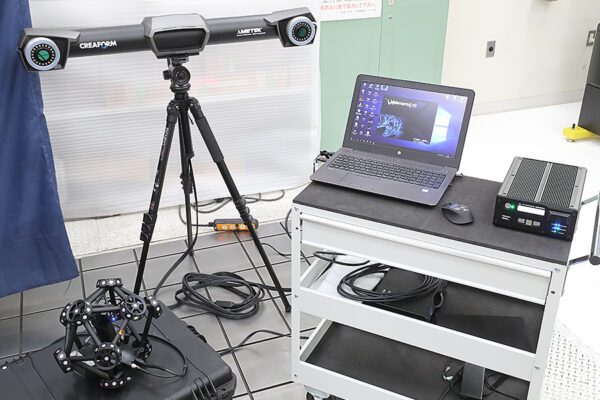
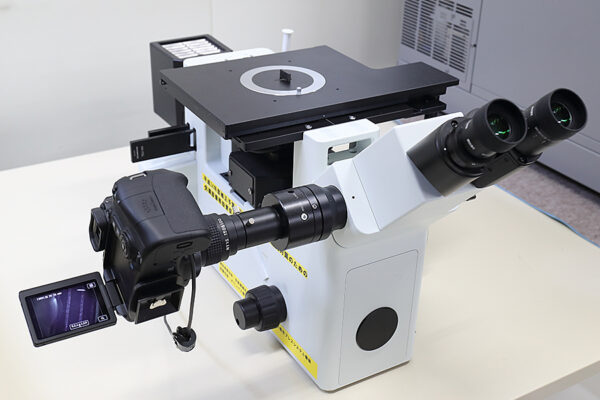
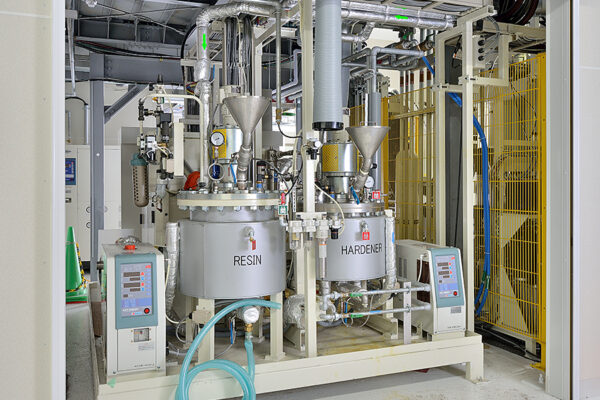
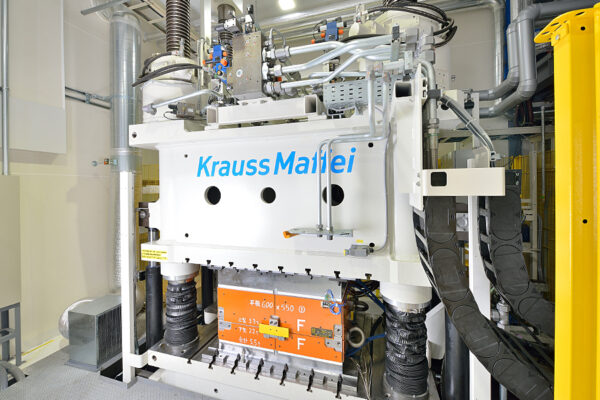
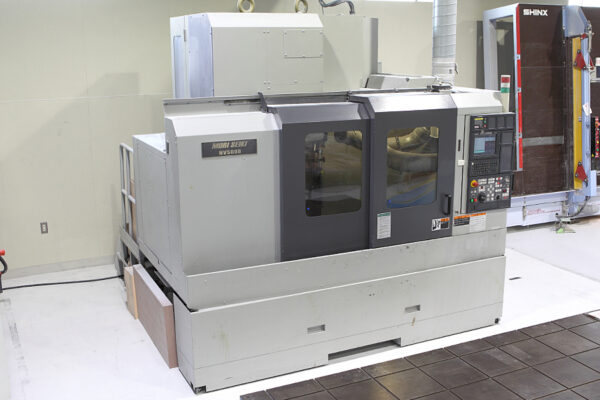
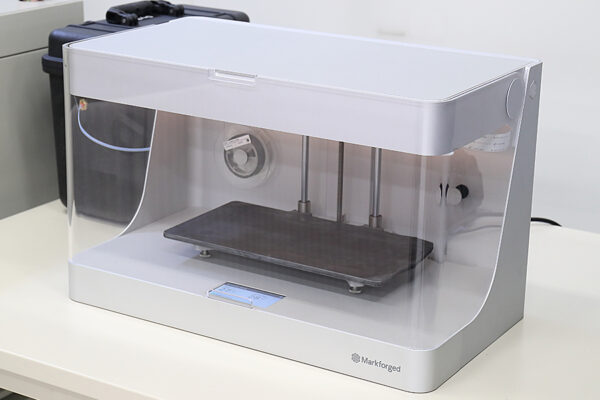
UCHIDA's equipment
We have cutting-edge equipment to ensure that we can address even the most advanced challenges of our customers.
Video Library
In the following video, we provide a detailed overview of our manufacturing process. Please feel free to watch and learn more.



































ピンバック: 【コラム】GFRPとは? | 株式会社UCHIDA
ピンバック: 【コラム】FRP・GFRP・CFRPの違いについて | 株式会社UCHIDA
ピンバック: 【コラム】炭素繊維とカーボンの違いについて | 株式会社UCHIDA
ピンバック: 【コラム】軽量化手法『FRP・GFRP・CFRP』 | 株式会社UCHIDA
ピンバック: 『FRP・GFRP・CFRP』マシニングセンタとは?【コラム】 | 株式会社UCHIDA