Introduction
These days, technical jargon such as FRP, CFRP, composites, and weight-efficiency often appear in the media for a range of applications. Such terms may be annexed with “lightweight, strong, and non-corrosive” materials that substitute metals. But what exactly are these materials?
Overview
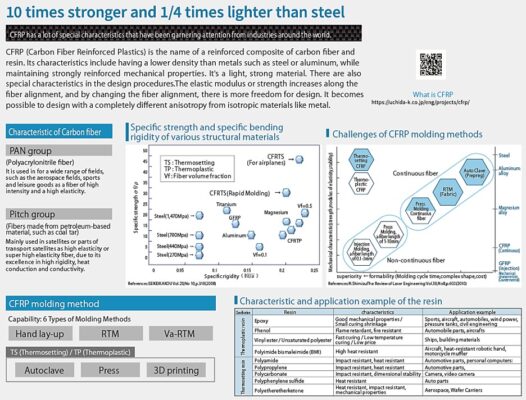
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP), as the name implies, refers to plastics reinforced with carbon fibers. The initial letter refers to the type of fiber used; C being carbon, G being glass fibers, and A being aramid fibers. Since CFRPs are composed from a combination of reinforcing fibers and resin (plastic), they are referred to as a “composite” or “composite material”.
This issue explores Oven Molding, one of the many methods for CFRP molding.
CFRP Molding Methods
Before delving into CFRP processing, let’s first look at molding methods. There is a wide variety of CFRP molding methods which are selected according to the desired application, shape/form, and production lot.
CFRP Molding Methods
Autoclave Molding
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding)
Va-RTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding)
Press Molding
Hand Lay-up Molding
Filament Winding Molding
Sheet Winding Molding
Pultrusion
3D Printer
At Uchida, we use the fabrication methods shown in red.
Autoclave Molding Method: The Hallmark of High-quality CFRP Product Manufacturing
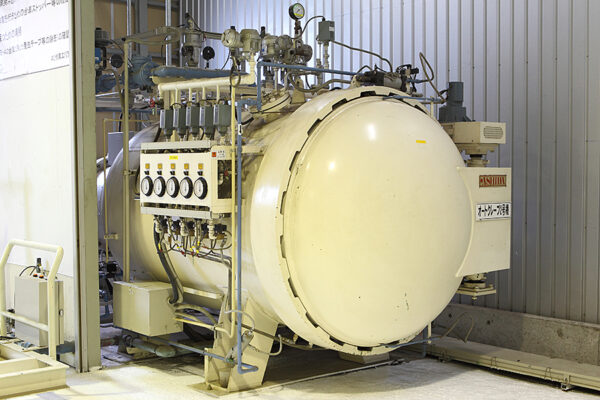
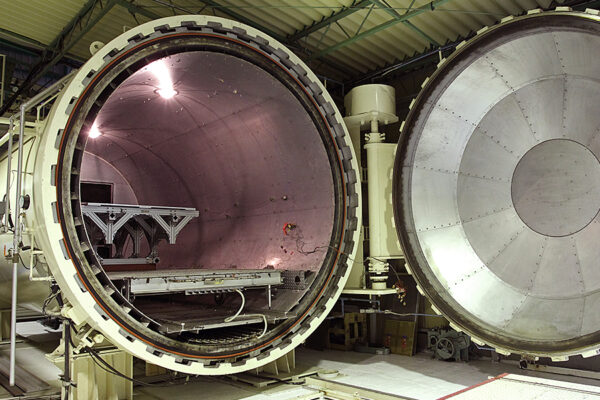
Despite the extensive range of molding methods, autoclave molding remains the hallmark method for design versatility and high-quality CFRP fabrication. High-quality CFRP created using the autoclave molding method is known as dry carbon. This method is suitable for prototyping and small-lot production as it does not require expensive metal molds.
Oven Molding is a thermo-compression molding whereby resin pre-impregnated carbon fiber sheets, called prepregs, are laminated sheet-by-sheet into a laminate stack, vacuum bagged, and then transferred to an autoclave where it is thermo-cured and pressurized.
YAOKI Laminate 01
Autoclave Molding vs. Oven Molding
What is Autoclave Molding?
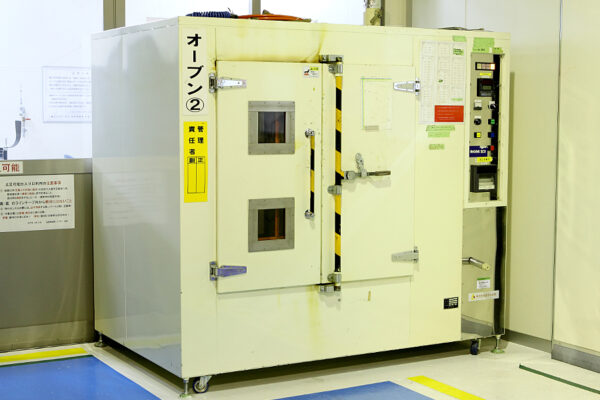
In a nutshell, this method employs the same materials, sub-materials, and processes as autoclave molding. The difference is that molding is performed in an oven, such as a hot air circulation oven, which serves to minimize temperature irregularities. In other words, it is one of the OOA, “Out of Autoclave,” methods developed for producing composites without an autoclave.
Autoclave molding is typically and widely leveraged in the aircraft industry due to its capacity to use stable, high-strength, and high-quality achieving prepregs, thereby producing products with minimal inconsistencies. Despite its popularity, autoclave molding has cons as well as pros.
Disadvantages of Autoclave Molding
- High initial investment in equipment (cost)
- Molding times of approximately 4-6 hours per item (productivity)
Various OOA manufacturing methods, molding equipment, and materials have been developed in recent years to mitigate the disadvantages attributed to autoclave molding, leading to further diversification of applied materials and characteristics. Of OOA methods, Oven Molding is one of the least complex.
Key Features of Oven Molding
(1) Can use the same prepregs and sub-materials as autoclave molding.
(2) Equipment and facility installation costs are lower than autoclave molding.
(3) Offers the same freedom for fiber orientation design as in autoclave molding.
(4) Can accommodate large products as in autoclave molding.
Downfalls Compared to Autoclave
(1) Lower capacity for complex shape molding, compared to autoclaving.
(2) Lower physical and mechanical properties than autoclaving due to the lack of applied pressure.
Manufacturing Method
CFRP exhibits diverse properties and is produced using a variety of molding methods depending on the product form, production lot, structure, and other factors. At Uchida, we handle a wide range of molding methods alongside one-stop support starting from prototyping.
Summary
Oven Molding is a CFRP processing method capable of producing high-quality products with comparatively low initial investment costs. This method leverages the same processes as autoclaving molding but uses an oven instead of an autoclave. That said, due to similar processes and use of prepregs, Oven Molding requires the same freezer storage facilities, clean room environments for lamination, and contamination prevention controls as in autoclaving molding.
While the lack of available information makes it difficult to understand the breadth of this advanced material, it can be best understood by its key characteristics— “lightweight, strong, and non-corrosive.” CFRP offers impressive advantages, but these also come with downfalls such as manufacturing complexity and difficulties with cost reduction, mass production, and recycling. We urge you to consider employing CFRP and GFRP with a complete view of its advantages and disadvantages side-by-side.
Related useful contents
You can explore related content by clicking on a topic of interest.
ABOUT UCHIDA - 55 years since our founding
We leverage a wealth of technical expertise as a CFRP molding and processing manufacturer using FRP, GFRP, and CFRP materials. We offer a one-stop solution, encompassing design, analysis, manufacturing, secondary processing, assembly, painting, quality assurance, and testing.
UCHIDA's equipment
We have cutting-edge equipment to ensure that we can address even the most advanced challenges of our customers.
Video Library
In the following video, we provide a detailed overview of our manufacturing process. Please feel free to watch and learn more.