Introduction
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP) is the preferred material for high-strength and low-weight-critical engineering applications such as aerospace, automotive and sporting equipment components. However, as CFRP is extremely hard and difficult to process, it requires specifically adapted m[U1.1]achining approaches and technical know-how. This column describes the main methods and their respective characteristics of CFRP processing technology.

Features of CFRP Machining
CFRP is a composite material consisting of a lightweight polymer resin reinforced with high-strength carbon fibers. While this composition achieves an incredible weight-to-strength ratio, the fibrous architecture of of the carbon fibers necessitates specialized and dedicated machining processes.
Once cured, the resin matrix becomes difficult to modify, creating challenges for post-processing precision adjustments and surface finishes.
Here are some points to keep in mind when machining CFRP:
– High Hardness: Once reinforced, the carbon fibers are not easily cut with ordinary tools.
– Dust Generation: Machining produces fine carbon fiber dust and resin particles
– Tool Wear: The hard abrasive nature of the carbon fibers accelerates cutting tools wear, reducing tool life.
CFRP Processing Methods
Mechanical Cutting
Mechanical cutting processes leverage drills, milling machines, or lathes to dimensionally cut and contour CFRP components. Proper selection of cutting speeds and parameters are essential in this method.
– Features: High-precision machining, machine contouring of complex shapes, and fine hole making.
– Key Considerations: Use tools with specialized coatings to reduce tool wear that occurs during cutting, and apply a cooling solution to prevent excessive heat generation.
Grinding
Grinding is primarily employed for surface finishing, smoothing, and refinement. Diamond or ceramic abrasive tools are often used for grinding due to the material’s hardness.
– Features: Precision finishing operations, tight tolerances, and surface preparation. Suitable for fine-tuning and smoothing CFRP surfaces.
– Key Considerations: Significant dust is generated during grinding, so careful consideration must be given to the work environment, ventilation, and exhaust systems.
Drilling
Drilling is the typical common method for cutting holes in CFRP. This method demands specialized CFRP drills to maintain accuracy and prevent the material fractures or fiber pull-outs (protrusions) at the entry and exit points.
– Features: Accurate and small-diameter hole formation.
– Key Considerations: Selection of dedicated drill bits and cutting parameters / speeds is crucial to achieve accuracy and prevent material damage.
Laser Machining
Laser machining, including CO2 and fiber lasers, is used for high-precision cutting and micro-drilling CFRP components. This method is particularly suitable for complex shapes and intricate details.
– Features: High-precision machining of complex shapes and geometry control with minimal thermal effects.
– Key Considerations: Thermal effects of laser processing may cause localized resin deformation or melting during processing. Consideration must also be given to the cooling systems and processing environment.
Hydraulic Cutting
Hydraulic cutting (water jet cutting) uses an ultra-high pressure water stream to cut the CFRP. This method offers precision cutting without thermal processes.
– Features: Precise cutting for intricate geometries (shapes), without the risk of thermal-induced deformation.
– Key Considerations: Hydraulic cutting may be slower than mechanical cutting and requires specialized cooling.
CFRP Machining Considerations
When machining CFRP, the following points should be noted:
– Tool Selection: CFRP machining require wear-resistant tools, such as Diamond-coated or ceramic tools, to manage rapid wear caused by the abrasive carbon fibers.
– Dust Control: Fine dust particles and powder generated during CFRP processing can be hazardous, and necessitates proper ventilation and dust control strategies. We recommend using dedicated dust collectors and masks.
– Thermal Control (cooling): High temperatures during machining can degrade or melt the resin. Cooling liquids are essential for proper temperature control.
Industrial Applications of CFRP Machining Technology
CFRP machining technology is widely utilized for weight-critical, high-performance applications such as the following:
– Aerospace Industry: Precision CFRP machining of structural aerospace components and engine parts requiring a high weight-to-strength ratio. Advanced CFRP machining technology is indispensable due to the high precision required.
– Automotive Industry: Machining of lightweight structural components—particularly in sports cars and electric vehicles—that employ CFRP to reduce vehicle weight.
– Sporting Equipment: CFRP machining and precision technology is employed to manufacture lightweight and high-performance sporting equipment such as bicycle frames, golf clubs, and skis.
Summary
CFRP machining and contouring of complex geometries is a highly sophisticated process requiring dedicated techniques, methods, and know-how. Each method—mechanical cutting, grinding, drilling, and laser machining—offers specific advantages as well as distinct engineering challenges. Precision machining techniques that effectively leverages the inherent characteristics and strengths of CFRP continue to evolve across industries, driving technological advancements and expanding the use of CFRP in new fields.
Related useful contents
You can explore related content by clicking on a topic of interest.
ABOUT UCHIDA - 55 years since our founding
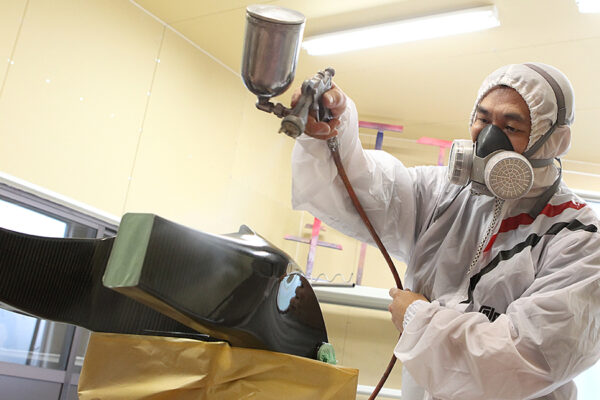
We leverage a wealth of technical expertise as a CFRP molding and processing manufacturer using FRP, GFRP, and CFRP materials. We offer a one-stop solution, encompassing design, analysis, manufacturing, secondary processing, assembly, painting, quality assurance, and testing.
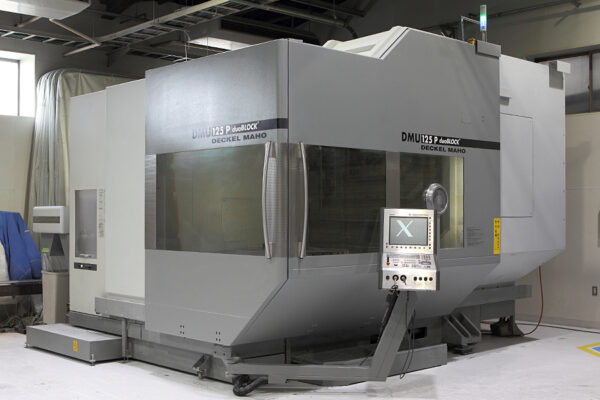
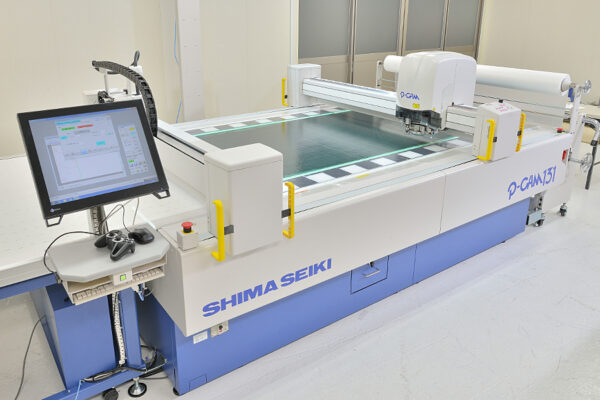
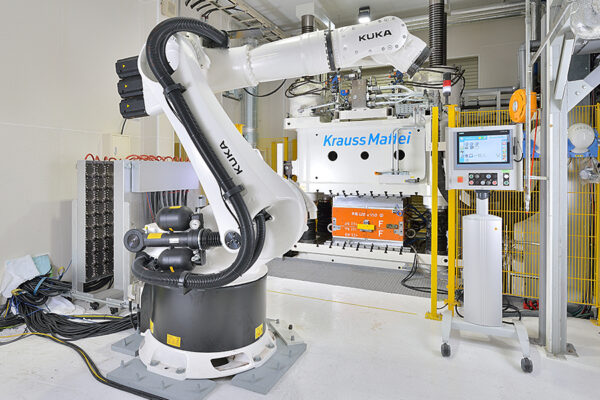
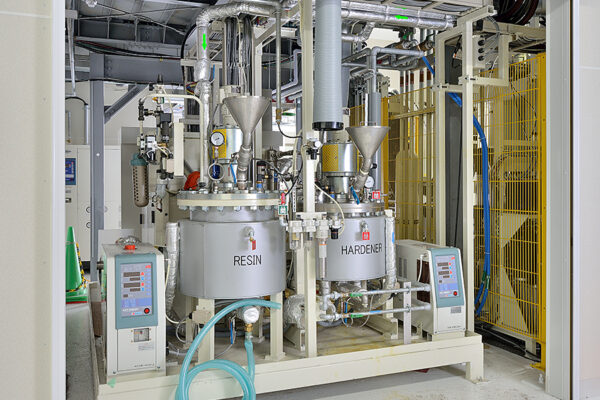
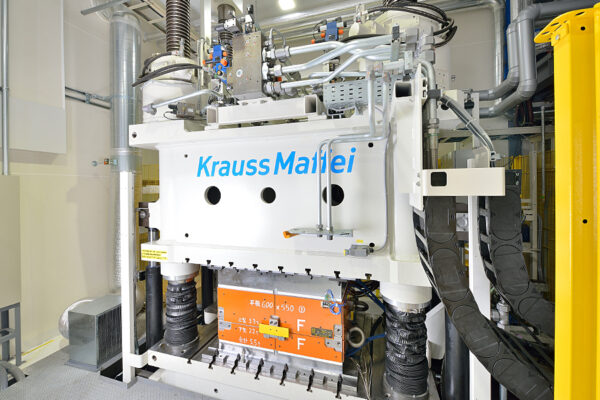
UCHIDA's equipment
We have cutting-edge equipment to ensure that we can address even the most advanced challenges of our customers.
Video Library
In the following video, we provide a detailed overview of our manufacturing process. Please feel free to watch and learn more.
Contact us