Introduction
The terms carbon composite or CFRP have become buzzwords is recent years. CFRP is equated with being robust, lightweight, and expensive, but what exactly is this material and how can be utilized for productization and commercialization?
What is Carbon? Delving into CFRPs
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics
While the term carbon fiber refers to thin strands of carbon, these fiber strands will not retain their form on their own. Thus, they are combined with a resin to retain the shape and maximize its distinct lightweight and strong characteristics. Composite materials are substances composed of two or more constituents, such as carbon fiber and resin, to yield new functions. Carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) is the name given to a composite created from carbon fiber and resin.
Carbon Composite
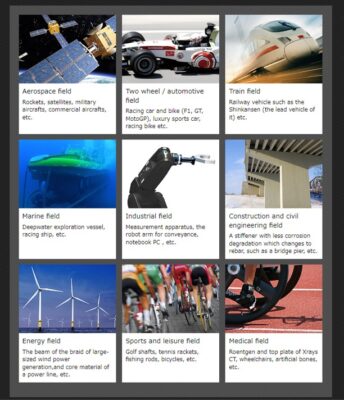
Carbon composite, also referred to as CFRP, is compound material that is produced using carbon. The distinctive “lightweight, strong, non-corrosive” qualities of advanced CFRP has opened doorways for leading-edge development in various fields, such as aviation, satellites, automobiles, and sporting and leisure equipment industries. Unlike metals and other isotropic materials, with CFRP, the strength is determined by the orientation of the carbon fibers (anisotropic) and therefore necessitates product-specific material design. The high degree of design versatility, in terms of resin and carbon-fiber constitution and arrangement, means that is volatile and difficult-to-handle without expert technical knowledge of the material and its properties.
Advantages and Disadvantages
As an anisotropic material, the strength of CFRP is determined by its fiber orientation. Thus, unlike metals and other isotropic materials, CFRP requires detailed material design and planning. The high design versatility of resins and fiber, however, necessitates specialized knowledge for fabrication. Working with these materials is nearly impossible without expert knowledge of their characteristics and functions. While CFRP offers impressive advantages, high production costs due to the need for molds, expensive materials, and complicated fabrication processes are lingering issues.
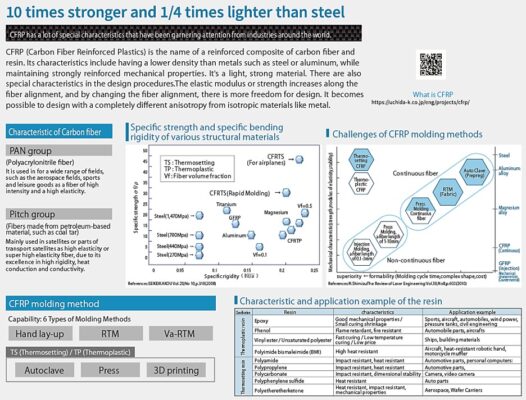
CFRP Molding Methods
Before delving into CFRP processing, let’s first look at molding methods. There is a wide variety of CFRP molding methods which are selected according to the desired application, shape/form, and production lot.
CFRP Molding Methods
Autoclave Molding
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding)
Va-RTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding)
Press Molding
Hand Lay-up Molding
Filament Winding Molding
Sheet Winding Molding
Pultrusion
3D Printer
At Uchida, we use the fabrication methods shown in red.
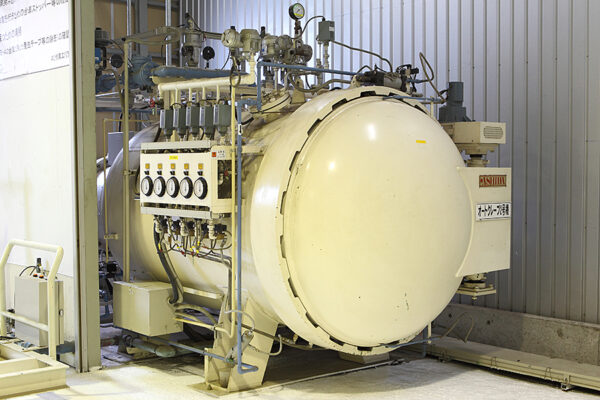
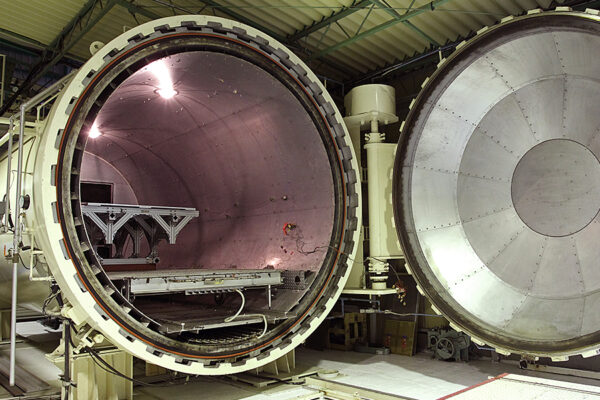
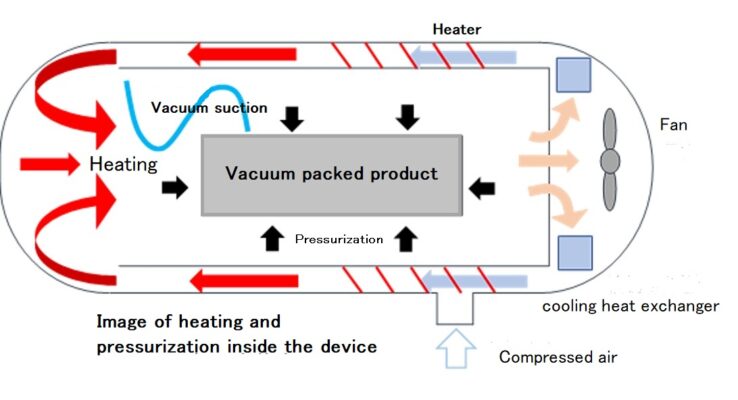
Autoclave Molding Method: The Hallmark of High-quality CFRP Product Manufacturing
Despite the extensive range of molding methods, autoclave molding remains the hallmark method for design versatility and high-quality CFRP fabrication. High-quality CFRP created using the autoclave molding method is known as dry carbon. This method is suitable for prototyping and small-lot production as it does not require expensive metal molds.

Autoclave Internal Thermal Heating and Pressurization Processes
Precautions When Handling CFRP
Anisotropic Material
Unlike isotropic materials such as metals, which have a uniform strength in all directions/orientations, the strength of CFRP varies depending on the orientation of the carbon fibers (anisotropic). Specialized knowledge, material designing, and lamination technique is thereby essential to ensuring that the product exhibits the required strength in the required direction.
Various Molding Methods/Manufacturing Processes
To recap, CFRP manufacturing methods vary according on numerous factors including the product material, shape, production lot, delivery time, and Vf (fiber content in volume).
Specialized Processes
CFRP is predominantly manufactured using the autoclave method. Ultra-thin 0.08 to 0.2mm sheets of carbon fiber which are pre-impregnated with resin matrix (referred to as prepregs) are layered into a laminate stack to form the product. With this method, any foreign matter or voids which form between the layers are not visibly detectable after molding is complete. This is referred to as a “special process.” With special processes, testing for any internal defects requires the use of non-destructive inspection techniques and strict process controls must be employed at each stage of the manufacturing process.
Summary
This article discusses carbon composite “CFRP” molding, which has been widely used in automobiles, sports, leisure, and other applications, including “flying objects,” where weight reduction is a high priority. That said, due to a lack of concrete information on manufacturing methods and costs, many people feel that the hurdles are too high. When consulting or inquiring about CFRP, contacting a manufacturer that is familiar with CRP and has a proven track record is a best way to get the results you are looking for.
Related useful contents
You can explore related content by clicking on a topic of interest.
ABOUT UCHIDA - 55 years since our founding
We leverage a wealth of technical expertise as a CFRP molding and processing manufacturer using FRP, GFRP, and CFRP materials. We offer a one-stop solution, encompassing design, analysis, manufacturing, secondary processing, assembly, painting, quality assurance, and testing.
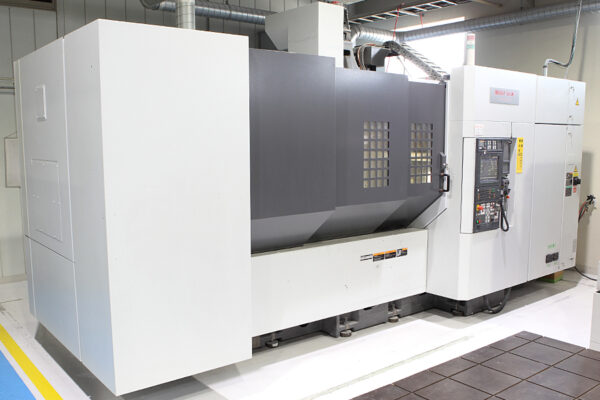
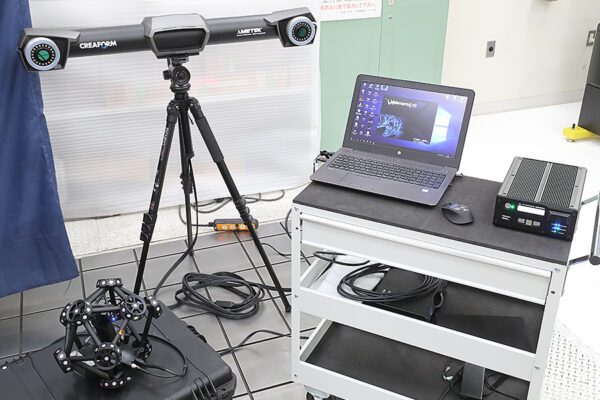
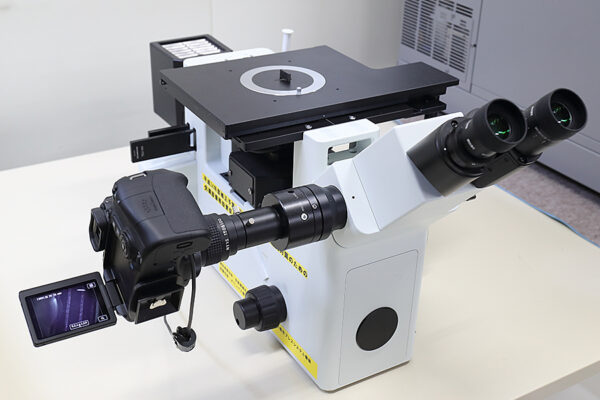
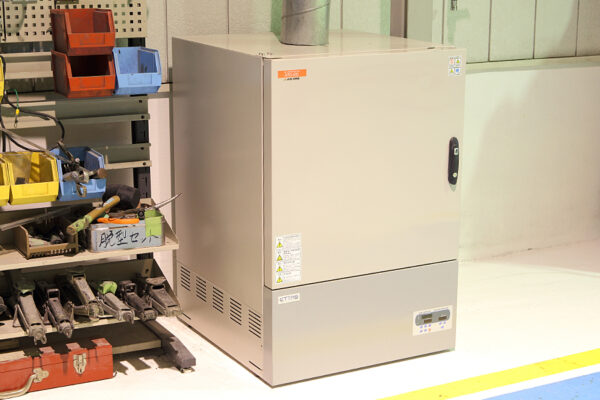
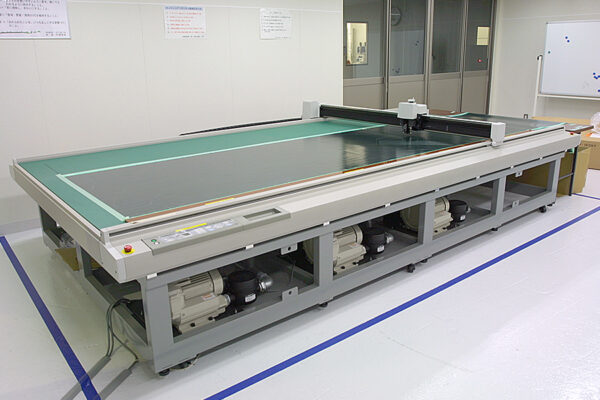
UCHIDA's equipment
We have cutting-edge equipment to ensure that we can address even the most advanced challenges of our customers.
Video Library
In the following video, we provide a detailed overview of our manufacturing process. Please feel free to watch and learn more.