What is CFRP? A Deeper Look at Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics
As per the name CFRP (carbon fiber reinforced plastic) is a composite material (type of FRP) whereby a plastic polymer base material is fortified with carbon fibers. The resulting distinctive “lightweight, strong and non-corrosive” qualities has made CFRP a leading material-of-choice across diverse industries and applications.
Carbon fiber itself is a fine yarn-like filament which exhibits exceptional strength but is unable to hold a form on its own. With the product known as CFRP or dry carbon, we composite these strength-obtaining carbon fibers with a plastic polymer to achieve a strong, highly elastic, and formable material.

CFRP Manufacturing Methods
CFRP offers considerable advantages, but what kinds of manufacturing methods are used to produce it? Here, we will introduce the hallmark molding method for CFRP— autoclave molding.
CFRP Molding Methods
Autoclave Molding
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding)
Va-RTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding)
Press Molding
Hand Lay-up Molding
Filament Winding Molding
Sheet Winding Molding
Pultrusion
3D Printer
At Uchida, we use the fabrication methods shown in red.
A wide range of molding methods for different applications, shapes, production lots, and so on.
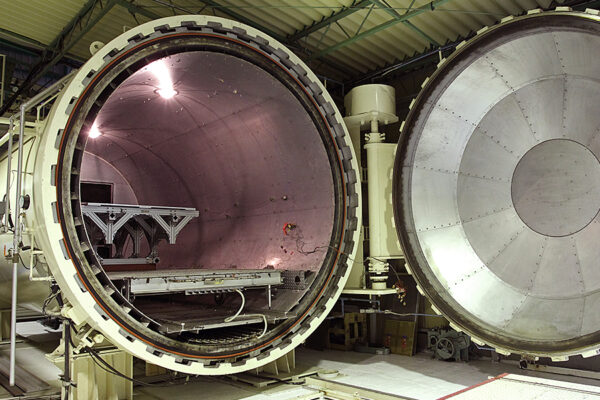
Autoclave Molding Method: The Hallmark of High-quality CFRP Product Manufacturing
Despite the extensive range of molding methods, autoclave molding remains the hallmark method for design versatility and high-quality CFRP fabrication. High-quality CFRP created using the autoclave molding method is known as dry carbon. This method is suitable for prototyping and small-lot production as it does not require expensive metal molds. The diagram below illustrates the production process of CFRP products using the autoclave molding method.

What are Prepregs?
The term prepreg refers to a carbon fiber sheet that is pre-impregnated with resin. Carbon fiber configurations is divided into two main types: Uni-directional (UD) carbon fiber fabric, whereby all the fibers run in a single direction, and woven carbon fiber fabric, whereby the fibers are woven into a fabric with interlacing yarns. There is a huge selection of carbon fiber fabrics from which we choose the optimal type for the structure of the item according to its required strength and rigidity. Likewise, for the resin matrix, we must carefully select the optimal type from a diversity of thermosetting or thermoplastic resin options. The characteristics and heat resistance of each resin will inform which type we employ for the job. The most common choice for CFRP products is the woven fiber fabric (plain weave or twill weave) with epoxy resin as the matrix.

Prepregs are intermediate materials in an uncured state.
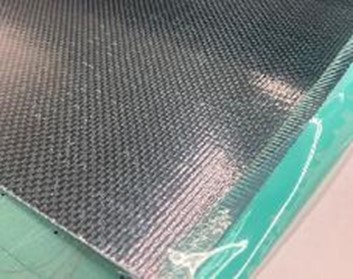
Prepreg Lamination (Lay-up)


Video on carbon prepreg lamination
[Matters of Caution When Laminating]
・Make sure to remove the protective film and backing paper.
→ Results post-molding defects.
・As an anisotropic material*, lamination of fiber reinforced plastics and CFRPs must strictly follow the design specification, fiber orientation, sequence, and vacuum degassing processes set out in the product design instructions.
→ While appearing identical with the same thickness, the final product will have vastly different mechanical properties.
→ Mistakes in lamination sequence may result in defects and deformations.
・Take care when laminating curved surfaces to prevent the fibers from wrinkling.
→ Cause defects such as uneven or changes in thickness after post-molding.
・Perform lamination in a clean room and take care to prevent any contaminates or foreign objects from mixing between the layers.
→ Lead to defects.
*An anisotropic material is a material whereby the strength of the material is determined by the orientation of the fibers.
Quasi-isotropic Lamination (Lay-up)
As an anisotropic material, carbon fiber reinforced plastics can be designed to exhibit the required strength in the required direction. Quasi-isotropic lamination (lay-up) is technique that orientates the fibers to achieve equal strength in all directions to simulate the isotropic properties seen in metals and other isotropic materials; hence the name quasi-isotropic. For this reason, with CFRP we need to tailor design the material to each product.
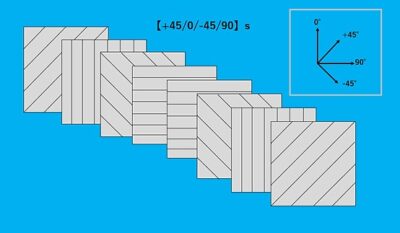
In quasi-isotropic lamination, we stack a total of 8 layers sequentially at +45°, 0°, -45°, 90°, 90°, -45°, 0°, +45°. We then eliminate any air trapped between the layers, during lamination, by vacuum degassing the stack.
Summary
This issue explains the CFRP quasi-isotropic lamination method using intermediary prepregs. We hope this offered you deeper insight into the key features of CFRP and lamination techniques.
Related useful contents
You can explore related content by clicking on a topic of interest.
ABOUT UCHIDA - 55 years since our founding
We leverage a wealth of technical expertise as a CFRP molding and processing manufacturer using FRP, GFRP, and CFRP materials. We offer a one-stop solution, encompassing design, analysis, manufacturing, secondary processing, assembly, painting, quality assurance, and testing.
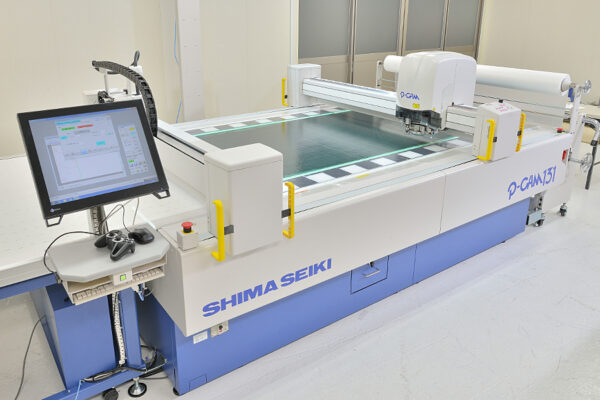
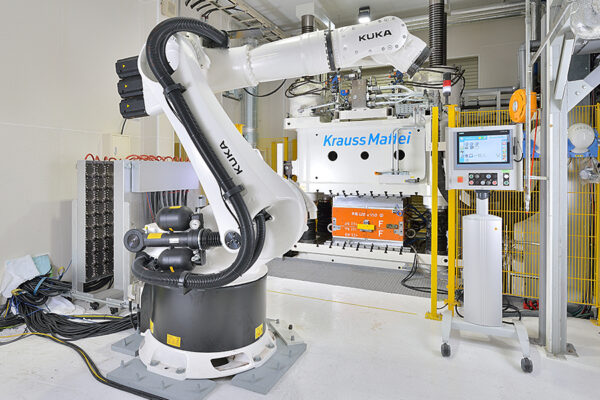
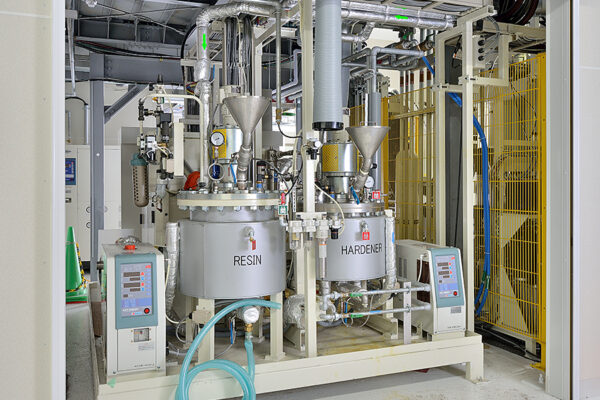
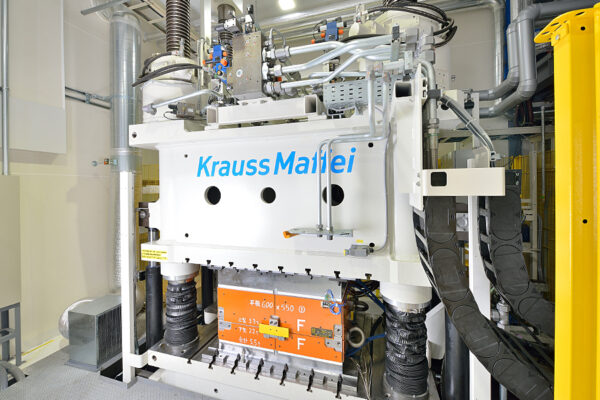
UCHIDA's equipment
We have cutting-edge equipment to ensure that we can address even the most advanced challenges of our customers.
Video Library
In the following video, we provide a detailed overview of our manufacturing process. Please feel free to watch and learn more.